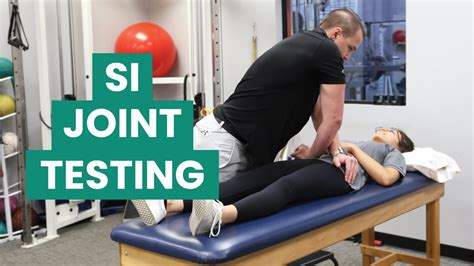
march test si joint anterior torsion|sij provocation special tests : distributors Here is how to correct an anterior torsion. The goal is to release the anterior (deep) side - the right side in our example - back into place. In our example, the left side is both fixated and more superficial, so the lesion is a left anterior . Resultado da Resultados de la Quiniela en Notitimba. Bienvenido a Notitimba, el sitio web líder en información sobre la quiniela en Argentina. Aquí encontrarás los .
{plog:ftitle_list}
17 de jan. de 2023 · All BitLife characters will eventually become a teenager, and you know what that means – it’s time to hit the road! BitLife lets players get their driver’s license .
The March Test, also referred to as Gillet Test or Stork Test, is one of the most commonly used motion related palpation test 7, 10). This test assesses the movement of the .Here is how to correct an anterior torsion. The goal is to release the anterior (deep) side - the right side in our example - back into place. In our example, the left side is both fixated and more superficial, so the lesion is a left anterior .
The Sacroiliac Joint Special Test Cluster, also known as the Cluster of Laslett, is a diagnostic tool used in the assessment of sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain. This test battery consists of 4 (or 5) tests designed to diagnose nociception in the .For example, an anteriorly directed force on the left of the sacrum at the level of the joint (S1, S2, and S3) induces a right rotational force and is a joint spring test. In contrast, right active .
FABERE (Patrick’s test) reproduction of pain with flexion, abduction, external rotation of the hip joint, and extension of the leg via downward force by the examiner. In a degenerative hip, . Clinical diagnosis of SIJ pain remains yet problematic. The cause of SIJ pain is multifactorial. The pain may be a result of an inflammatory disease, arthrosis, traumatic injury, .[Purpose] The March Test (MT), evaluating hypomobility of the sacroiliac joint (SIJ), is often used in clinical practice to evaluate low back pain but has limited reported validity and . To review the anatomy and function of the sacroiliac joint (SIJ), as well as the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnostic criteria, and treatment options for SIJ .
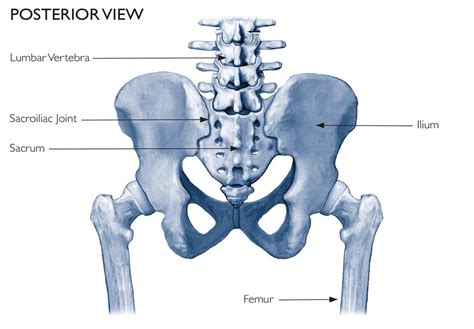
The sacroiliac joints are located on each side of the spine between the two pelvic bones, which attach to the sacrum. The main function within the pelvic girdle is to provide shock absorption for the spine and to transmit forces between the upper body and the lower limbs. The SI joint .
P a g e | 2 Hesch Institute March 2012 www.Heschinstitute.org Email: [email protected] ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS I would like to thank our Creator, my parents Reuben and Bernadine Hesch (both deceased) for
For a test to be positive, it must reproduce the patient’s typical pain in their SI joint region. While 1 positive test raises suspicion, 3 or more positive tests would indicate the SI joint as a pain generator. . Applies tensile force on the anterior aspect of the SI joint on the side tested.If there is an anterior innominate, the leg that appeared longer will shorten with the sit up. Diagnostic Accuracy: Sensitivity: .44; Specificity: .64 ("Four clinical tests of sacroiliac joint dysfunction: the association of test results with innominate torsion among patients with and without back pain"). The data do not support the value of these tests in identifying innominate torsion, although the use of these tests for identifying other phenomena (eg, sacroiliac joint hypomobility) cannot be . Sacroiliac joint dysfunction should be diagnosed and treated before any surgical intervention,³⁻⁵ because once the SI joint has been fused in a non-anatomical position, correction is not possible. SI joint dysfunction is the primary cause of 25% to 50% of significant chronic low back pain3 and should be corrected before considering surgery.
The data do not support the value of these tests in identifying innominate torsion, although the use of these tests for identifying other phenomena (eg, sacroiliac joint hypomobility) cannot be ruled out. Further exploration of the association of Gillet test .Purpose: To assess mobility limitation in the sacroiliac region. Test Position: Standing. Performing the Test: The examiner palpates the inferior aspect of the PSIS of the tested side with one hand and the S2 spinous process with the other. The patient flexes the hip past 90 degrees. The examiner should feel the PSIS move inferiorly and laterally relative to the sacrum.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like March Test/ Gillet's Test, Standing/Sitting Flexion, Supine-to-sit and more. . -RF attaches to AIIS and if tight will cause pelvis to move into an anterior pelvic creating torsion at .The standing flexion test is a test that can be used to assess sacroiliac joint dysfunction. It is best used in combination with other specific tests. A synonym is the Vorlauf test. . The purpose of the standing flexion test is to assess sacroiliac joint dysfunction. This condition can result from a variety of causes, including .
The way people sit often causes issues with the pelvis and this translates into pain when people are sitting. Clients often complain of pain in their lower back or pelvis, which can easily be addressed by getting them to sit correctly. One of the common complaints when sitting is a pain, but this comes in many forms from pain when sitting, pain when getting up and . Some things to keep in mind when assess the sacroiliac joint: It is difficult to palpate the deep SI joint, making reliability and validity challenging; The reliability of assessing symmetry, SI joint motion, and SI joint position also has poor reliability; Pain along the Fortin Area without pain in the Tuber Area may indicate SI joint painAfter watching this video you will be able to:1. Describe Symmetrical vs Asymmetrical Sacroiliac Joint Movement2. Describe Nutation as the movement of the Sa.
Purpose: tests for functional leg length difference resulting from pelvic dysfunction Procedure: Pt. lies supine with legs straight and medial malleoli level. Pt. is asked to sit up while examiner observes whether one leg moves proximally further than the other. + Result: one leg moves more proximally than the other, indicating pelvic torsion or rotation Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction is a degenerative condition of the sacroiliac joint resulting in lower back pain. Diagnosis is made clinically with pain just inferior to the posterior superior iliac spine that is made worse with .The sacral thrust test is a pain provocation test used to diagnose sacroiliac dysfunction. One single positive test does not have high diagnostic accuracy but a combination with other sacroiliac pain provocation tests gives valid .
Angle of the sacroiliac joint “wedges”the sacrum in an anterior direction Prevents posterior movement Dorsal (posterior) sacroiliac ligaments much stronger than anterior sacroiliac ligaments Purpose: counteract significant pelvic forces pushing apex . (AKA Backward torsion ) b. Negative test = If there is springing allowed = Neutral . Treatment of sacroiliac_joint_dysfunction_nata - Download as a PDF or view online for free . tests, and pain provocation tests are described. Common sacroiliac joint dysfunctions like forward and backward sacral torsion are discussed. Read less. Read more. Report. Share. Report. . (GilletGillet’’ss march test)march test) –– PSIS .
sij provocation special tests
sacral torsion of si joint
Stork test (Gillet’s march test) – PSIS should drop (also move laterally after 90°) Hip drop test – Anterior nutation on side of bent knee, rotate toward lumbar concavity Side bending – Anterior nutation on side of convexity, rotate toward lumbar concavity – Anterior innominate rotation (side of .
PT Classroom - SI Joint "Simplified" ׀ by Steve Bayer, MSPT, ATC, CSCS, FAAOMPT Steve Bayer, MSPT, ATC, CSCS, FAAOMPT received his B.S. in Exercise Science in 1995 from the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, he earned his Master’s degree in Physical Therapy in 1998 from the University of Miami, focusing his practice in the areas of orthopedic and sports .Key indexing terms: Leg length inequality, Sacroiliac joint, Torsion, Mechanical, Posture, Ilium. . in turn suggesting a 3.2° range of motion for each sacroiliac joint from extreme anterior to posterior rotation. The amount of torsion was found to be “dose related.” . (aka Gillet) test. 38.

sacral side of si joint pdf
Purpose: To assess for hypomobility of the sacroiliac joint. Test Position: Standing. Performing the Test: The examiner places one hand on the test side's PSIS and the other hand on S2 spinous process. The patient then bends forward. The test is repeated on the opposite side. A positive test occurs when one PSIS is noted to move in the superior direction more than the .
right sacral side of si joint
The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) is the largest axial joint in the body. It connects the spine to the pelvis and transfers load between the lumbar spine and the lower extremities. Research has shown the sacrum has very little movement. Numerous ligaments across the joint support and limit movement of the SIJ.2 Szadek KM, van der Wurff P, et al. Diagnostic validity of criteria for sacroiliac joint pain: a systematic review. J Pain. 2009;10(4):354-68. The iFuse Implant System® is intended for sacroiliac fusion for conditions including sacroiliac joint dysfunction that is a direct result of sacroiliac joint disruption and degenerative sacroiliitis.The test was designed to detect sacroiliac joint dysfunction, which is defined as a sacroiliac joint that is “blocked” and thus not moving. However, like many other palpation tests, the Gillet test has a low reliability with a kappa value of 0.22 according to Dreyfuss et al. in the year 1996. The same authors report a sensitivity of 43% and . One hand is placed directly on the sacrum and is being reinforced by the other hand. Purpose is to apply an anterior shear force to both sacroiliac joints since the ilia are fixed by the examination bench. The test is positive if pain is reproduced in the sacroiliac region Laslett et al (2005) Also known as sacral compression test, downwards .
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The pelvis is formed by pairs of three fused bones and joined anteriorly by which of the following? a.Ischial tuberosity b.Pubic symphysis c.Sacroiliac (SI) joint d.Anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS), Which structure is responsible for stabilizing the pelvic girdle?a.Ischium b.Pubis c.Ilium d.Sacrum, The .
anterior lateral torsion correction
• 1 mo. ago. Ruisus. Rekkyo Sensen Chapter 0: The Chapter 0 of the new manga: Rekkyo Sensen (The Doomsday is Wartime). Portuguese-Mangadex: .
march test si joint anterior torsion|sij provocation special tests